Did you know that the Bitcoin halving event is expected to reduce miners’s rewards by 50%? The last event occurred in April 2024. This event is very important for miners and traders, as it is a moment when the block reward for mining new bitcoins is halved. This will impact miners and the market alike.
Key takeaways:
- Bitcoin halving is an event that cuts miner rewards in half every four years. This reduces the number of new bitcoins entering circulation, potentially driving up the price due to scarcity.
- The next Bitcoin halving is expected in 2028.
- Bitcoin halving also impacts miners, making it more difficult for less efficient miners to stay profitable. This could lead to consolidation in the mining industry.
- Bitcoin halving is a key mechanism for controlling the supply of new bitcoins and is designed to ensure that the total supply of Bitcoin does not exceed 21 million
What is Bitcoin Halving?
For those new to Bitcoin (BTC), the coin was created in 2009 by someone using the name Satoshi Nakamoto with the goal of making a digital currency without a central authority.
Approximately every 4 years, or every 210,000 blocks, the Bitcoin network undergoes a process called “halving,” meaning that the amount of BTC miners receive for validating transactions is reduced by 50%.
A block is a file containing 1 megabyte (MB) of Bitcoin transaction records on the Bitcoin blockchain. These groups of miners add a block by solving a difficult mathematical problem using specialized hardware.
To conclude the process and lock the block, they produce a random 64-character output known as a “hash”. Miners receive BTC compensation after completing these blocks.
In simple terms, Bitcoin halving means the Bitcoin network will reduce the number of new BTC tokens that enter circulation.
Originally, the total block reward was 50 BTC, but after the first Bitcoin halving in 2012, it was reduced to 25 BTC. After 4 years, it was reduced to 12.5 BTC; in 2020, it was left at 6.25 BTC. After the halving in April 2024, it was reduced to 3.125 BTC.
Bitcoin Halving History and Dates
To understand how it works, we will take a look at the history of Bitcoin halving events.
When was the first Bitcoin halving?
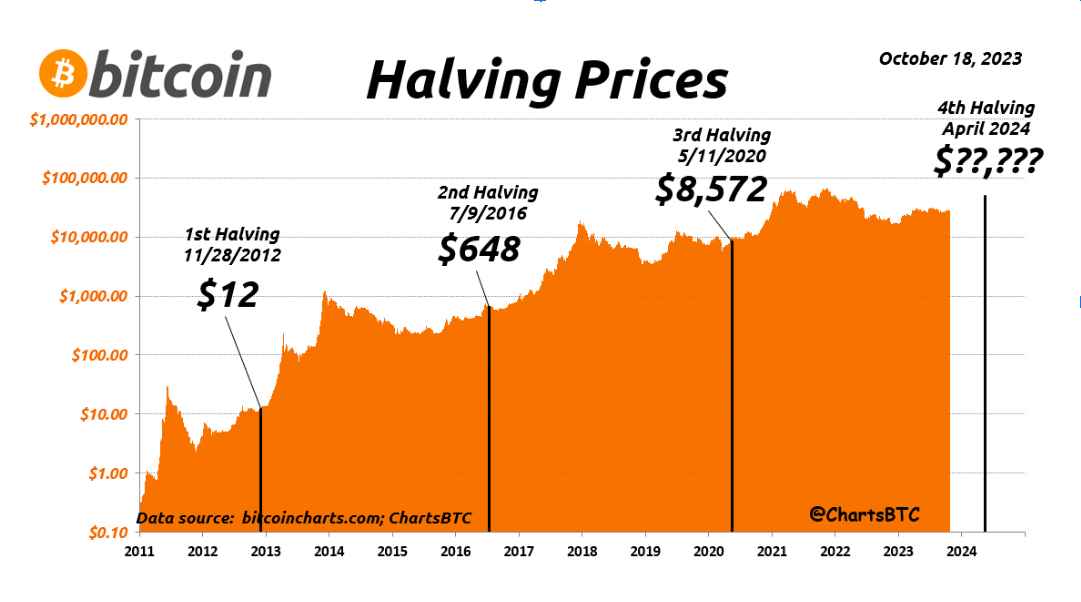
On November 28th, 2012, the first halving occurred when SlushPool, a miner using a Radeon HD 5800, mined the 210,000 block. This reduced the block from 50 BTC to 25 BTC. The price on the day of the halving was $12.35, and after 150 days, it increased to $127. Bitcoin price surged to $1,152 within a year, a remarkable increase of over 8,800%. This might be related to the overall growth of the cryptocurrency market during this period.
Subsequent Halving Event
On July 9th, 2016, the 420,000th block was formed, and the second halving occurred. This reduced the block from 25 BTC to 12.5 BTC per block. After 150 days, the price increased from $650.63 to $758.81.
Due to a more mature market with a higher baseline price. Price increase was less dramatic compared to the first halving. It reached $2,500 within a year, representing a 285% increase.
After approximately four years, the third halving occurred on May 11, 2020, and the block was reduced from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC. However, as of the day of the halving, the price of BTC increased from $8821.42 to $10,943 after 150 days.
Unlike the previous two halvings, the immediate price increase wasn’t as prominent. However, a substantial bull run began later in 2020, with Bitcoin reaching new all-time highs above $60,000 USD in 2021. This delayed effect could be attributed to various factors, including the global pandemic and institutional investment.
With the price increase after the three consecutive halves, miners and traders witnessed the fourth halving, which is one of the most important events in the crypto community this year. The fourth halving reduced the block from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC.
When Is the Next Bitcoin Halving Event?
The next havling will take place in 2028. The data from previous coin halving events show that the BTC price always increases after every halving. The increase goes higher and gets stronger with time. According to the historical data above, we might expect BTC to increase in price in 2028.
Why Bitcoin Halving?
According to Nick Szabo, a legal scholar and cryptographer, “the halving is a fundamental aspect of Bitcoin’s design. It helps to ensure the coin’s long-term viability as a store of value.”
Satoshi Nakamoto, the inventor of Bitcoin, created it as a digital currency. He designed a protocol for the coin to reduce its scarcity over time. Reducing the mining rewards by half decreases the rate at which new Bitcoin is generated.
Precious metals like gold have value and are created to be scarce. This is similar to Bitcoin; due to its finite supply, the digital currency was created to be scarce and drive up value over time.
Satoshi aimed to combine Bitcoin scarcity, its finite supply (21 million), and how the supply is controlled through halving, contributing to a valuable digital asset and a value proposition as a hedge against inflation.
This mechanism was implemented to control the Bitcoin inflation rate and create scarcity, which can increase its value over time.
The last halving, which took place in April 2024, gathered attention globally. However, traders in the crypto space are still debating the potential effect of the halving process on Bitcoin’s price, supply, and demand.
Potential Risks and Challenges Associated with Bitcoin Halving
Bitcoin halving, with the aim of maintaining scarcity and potentially increasing the value of the coin, also introduces potential risks and challenges for the crypto community. Here are some potential impacts of Bitcoin halving:
Security
Bitcoin miners use sophisticated computer machines like ASIC to verify transactions and create blocks. This group of people connect their computers to the Bitcoin network as nodes to verify transactions that are necessary for the network’s functionality. In return for verifying transactions on the Bitcoin network, they get rewarded.
Increased Transaction Fees
Bitcoin halving has the potential to increase transaction fees due to a simple supply-and-demand dynamic. Since Bitcoin miners secure the network by validating transactions, they receive newly minted Bitcoins along with transaction fees included in each block as a reward for their work. If competition for block space intensifies, the average transaction fee on the network might increase over time.
Market Volatility
Since the Bitcoin halving event is highly anticipated by crypto, it can introduce significant volatility to the market, impacting the price in both the short and long term. As the date of the halving event approaches, investors and traders might rush to buy Bitcoin in anticipation of future price increases due to scarcity. This can cause a bullish impact in price in the lead-up to the halving.
Miner Competition
Miners are very important to the Bitcoin network because, without them, the system will collapse, the value will go down, and security might be tampered with. The more miners that use nodes connected to the network, the more secure it is.
Halving impacts the network’s security by driving away less productive miners and increasing competition by decreasing mining rewards. After halving, miners would have to compete with others for limited block space, which might increase fees.
With reduced miner rewards, this aggressive competition amongst themselves could drive up transaction fees, especially for transactions needing faster confirmation times. The impact on miner fees is not guaranteed and may vary depending on many other factors.
Impact on miners
To compete with other miners during halving, miners must be more efficient and optimize their operations to stay profitable. Hence, upgrading their mining hardware and software ultimately strengthens the health and security of the Bitcoin network.
Alternatively, miners who are less productive and use less efficient equipment could be forced out of the industry, and larger, more efficient miners could control a bigger share of the network.
Bitcoin halving can trigger where mining takes place. Miners seeking the most cost-effective operations may relocate to areas with cheaper electricity, potentially including regions with a higher focus on renewable energy sources. This could lead to a decline in mining activity in current hubs and a more geographically distributed network overall, with government policies also playing a role in attracting miners.
Supply and Demand
As miners navigate the path to the last Bitcoin, mining will continue until the maximum supply of BTC reaches 21 million, which is estimated to happen around the year 2140.
This means the final halving is expected to occur in 2140, after which miners can no longer create new BTC and will receive rewards only from transaction fees.
Once 32 halvings occur in the Bitcoin network, there will be no other halving again. Hence, the major reason for halving is to ensure that the total supply of Bitcoin does not exceed 21 million.
It is a key mechanism to control the supply of new BTC entering circulation. The formula is that the total amount of BTC in circulation equals the maximum supply that has been programmed for it.
How Does Bitcoin Halving Work?
New bitcoins are mined approximately every 10 minutes. Approximately 900 new bitcoins are mined daily to be added to the total supply, and we have about nearly 89% (19 million bitcoins) of the total 21 million bitcoins that have already been mined and in circulation.
It uses an algorithm that allows network machines to compete to validate transactions using a method known as “mining’ and reward the mines with new BTC until a decentralized network of validators can verify the transactions are legitimate.
The first miner to successfully solve the mathematical equation can verify the respective block of transactions. Miners will receive newly minted Bitcoin for a total reward of 6.25 BTC.
The network is coded with half the payout miners received per 210,000 bytes after checking the groups known as “blocks” to confirm if the transactions are verified.
Conclusion
As we prepare for the next Bitcoin halving event, you should note that halving has major implications for miners as the competition in the mining ecosystem continues.
With Bitcoin’s limited supply and a mechanism that gradually reduces new coin creation, its inherent scarcity mirrors precious metals like gold, potentially driving long-term value appreciation.
Beyond value growth, it also acts as an inflation hedge, and its properties make it a potential store of value. While the future is uncertain, the halving mechanism, though initially challenging miners, strengthens network security and positions Bitcoin with unique characteristics that could redefine finance.
Disclaimer: The article is written for educational purposes only not intended as, and shall not be construed as, financial, investment, or trading advice. Some of the links in the article are links to third-party websites or other content for information purposes only. The affiliate links in the article will give us a commission with no additional cost at your end. For example if you click on an any of the affiliate links, and sign up and trade on changeNOW, Yinksmedia may receive compensation.
Yinksmedia does not recommend that any cryptocurrency should be bought, sold, or held by you. We advise readers to do their own research before trading any cryptocurrencies and invest wisely. Yinksmedia is not liable for investment gains or losses.

